
In an age where connectivity is omnipresent, safeguarding our digital boundaries has become paramount. Among the crucial defenses in this realm stands the Firewall configuration—an indispensable guardian fortifying our systems against an array of potential threats.
What is a Firewall?
A Firewall serves as a barrier between your computer/network and the vast, potentially hazardous expanse of the internet. Much like a security checkpoint, it monitors incoming and outgoing traffic, permitting or blocking data packets based on predefined security rules. This vital piece of software discerns between safe and malicious activity, curbing unauthorized access and protecting sensitive data from cyber threats.
The Role of Firewalls
Firewalls come in various forms, from software-based solutions integrated into operating systems to dedicated hardware appliances. Regardless of the form, their role remains consistent: shielding devices and networks by filtering traffic, preventing unauthorized access, and minimizing the risk of cyber attacks.
Setting Up a Basic Firewall
By default, SSH connections are typically established through Port 22 (TCP). The main advantage of using the default SSH-2 protocol (compared to VNC) is the encrypted connection using an AES algorithm with a 128-bit key length. Therefore, it is generally recommended to use SSH instead of VNC whenever possible.
In Linux, you should consider using the built-in software package ‘iptables’, which comes with the initial installation on most distributions by default.
There are two main advantages to using iptables:
-
The required software package is installed by default on most Linux distributions.
-
It is compatible with any Linux distribution (Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS, etc.) without restrictions.
You can also define IPv4 and IPv6 rules according to your own needs.
Checking the Current Firewall Configuration
Before configuring your firewall, there are no rules defined. To check this, use the following command:
iptables -LThe output will look similar to this:
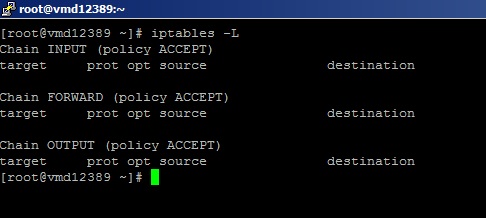
As you can see, there are currently no rules defined. The Software-Firewall will not block anything.
Adding Firewall Rules
To add firewall rules, use the following syntax:
iptables <ADD: -A> | <Chain: INPUT / Output> | <Source/Destination: -d / -s> | <action: -j> | <Art: ACCEPT>Here’s an example of how to use the iptables command to allow incoming traffic at port 80:
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -j ACCEPTExample Firewall Configuration for Linux
Here is an example script that will open the most commonly used ports on your Linux server:
#!/bin/bash
# Delete the current firewall setup:
iptables -F
# Define default rules for all chains:
iptables -P INPUT DROP
iptables -P FORWARD DROP
# Allow incoming/outgoing localhost frames for tests (e.g. Webserver, Mailserver):
iptables -A INPUT -d 127.0.0.1 -j ACCEPT
iptables -A OUTPUT -s 127.0.0.1 -j ACCEPT
# Allow loopback frames for the internal process management:
iptables -A INPUT -i lo -j ACCEPT
# Allow incoming/outgoing related-established connections:
iptables -A INPUT -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
iptables -A OUTPUT -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
# Allow incoming PING-Requests:
iptables -A INPUT -p icmp -j ACCEPT
# Allow incoming SSH connections:
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPT
# Allow incoming HTTP/HTTPS requests:
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -j ACCEPT
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 443 -j ACCEPT
# Allow incoming DNS requests:
iptables -A INPUT -p udp --dport 53 -j ACCEPT
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 53 -j ACCEPTTo use this script:
-
Login to your Linux server as root.
-
Create a shellscript with this command:
nano firewall.sh-
Paste in the content shown above.
-
Save the file with [CTRL] + O and exit the editor with [CTRL] + X.
-
Make the script executable with this command:
chmod +x firewall.sh- To run the script and open the ports provided by the script, use the following command:
./firewall.shMaking the Firewall Rules Permanent
Please note that if you use the sample script, all firewall rules will not be added permanently. After a server reboot, every rule would have to be set manually again.
To make the firewall rules permanent, you can run the following commands depending on your operating system:
Permanent Firewall Settings for CentOS 7 or higher:
yum install -y iptables-services
systemctl stop firewalld
systemctl mask firewalld
systemctl enable iptables.service
systemctl -t service | grep iptables
/usr/libexec/iptables/iptables.init savePermanent Firewall Settings for Debian/Ubuntu:
apt-get install iptables-persistent netfilter-persistent
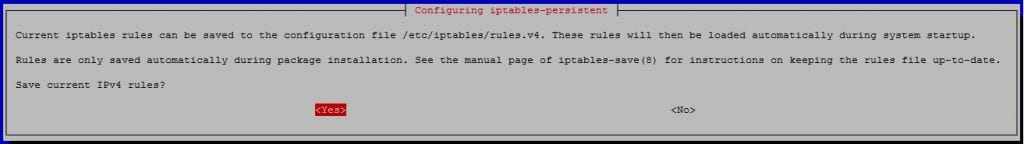
Saving the Current Firewall Configuration
You can also save your currently configured firewall rules if you have not saved them to the above files with this command:
iptables-save > /etc/iptables/rules.v4 && ip6tables-save > /etc/iptables/rules.v6
Restoring a Backup of the Firewall Configuration
We strongly recommend creating a backup of the current firewall setup to be able to immediately restore the previous configuration (e.g., connection locks).
To save your current IPv4/IPv6 firewall setup into a backup file, use the following commands:
iptables-save > /root/iptables_rules
ip6tables-save > /root/ip6tables_rulesTo restore the backup files, use:
iptables-restore < /root/iptables_rules
iptables-restore < /root/ip6tables_rulesRestoring Access to a Server with a Misconfigured Firewall
If you need to reconnect to your server due to a misconfigured firewall setup, you could use your VNC connection for your VPS to restore a previous configuration.
If you have a Dedicated Server, VNC access is not possible. You will have to reboot your server into the Linux rescue system to regain access.
Setting up a Basic Firewall for Windows
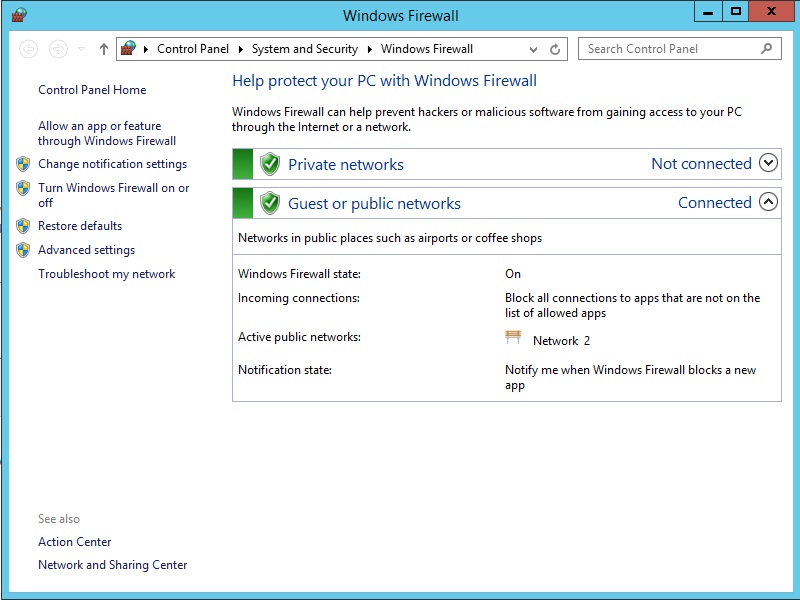
The Windows Firewall can be found within the Server-Manager settings as follows:
Windows-Firewall -> Public: On-> Advanced settings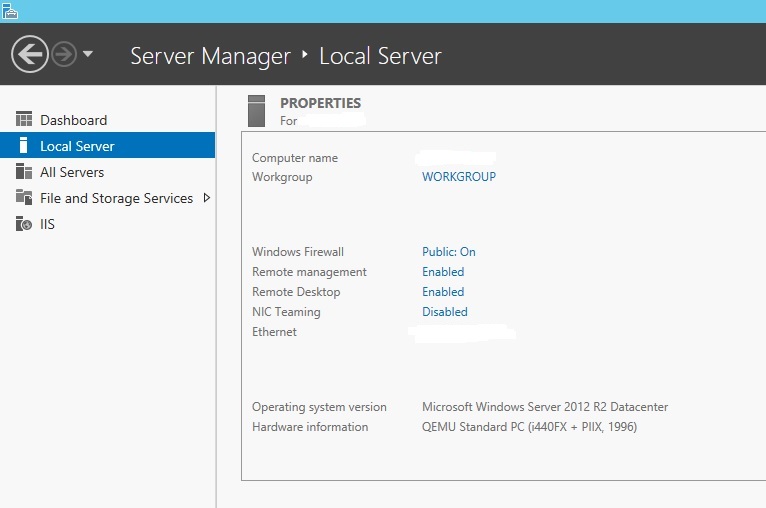
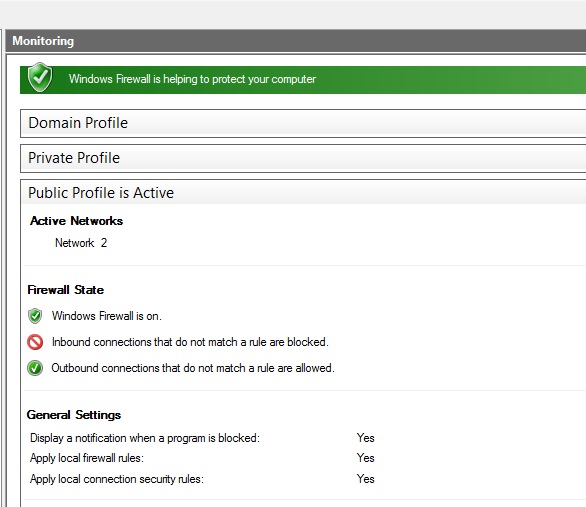
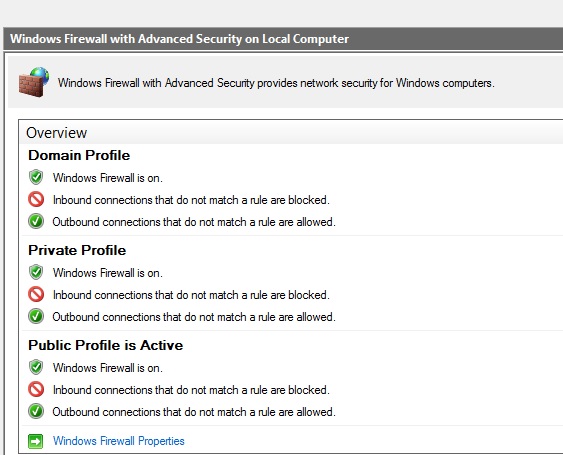
You can now modify your firewall rules according to your own needs.
The main difference between Linux and Windows is that Windows provides a basic firewall configuration by default. In most cases, it should be enough to keep the default setup or modify existing rules.
All active firewall rules are marked with a green tag. The rest of the rules (without any tag) need to be activated if required. Feel free to customize the firewall setup according to your own needs.
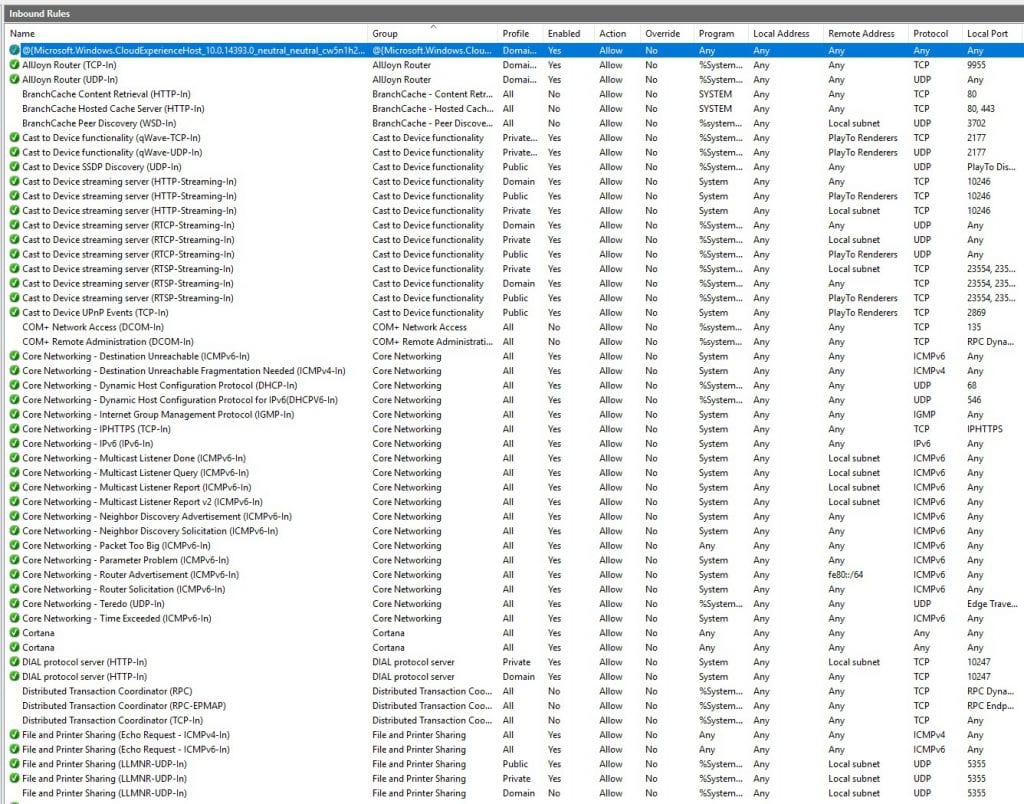
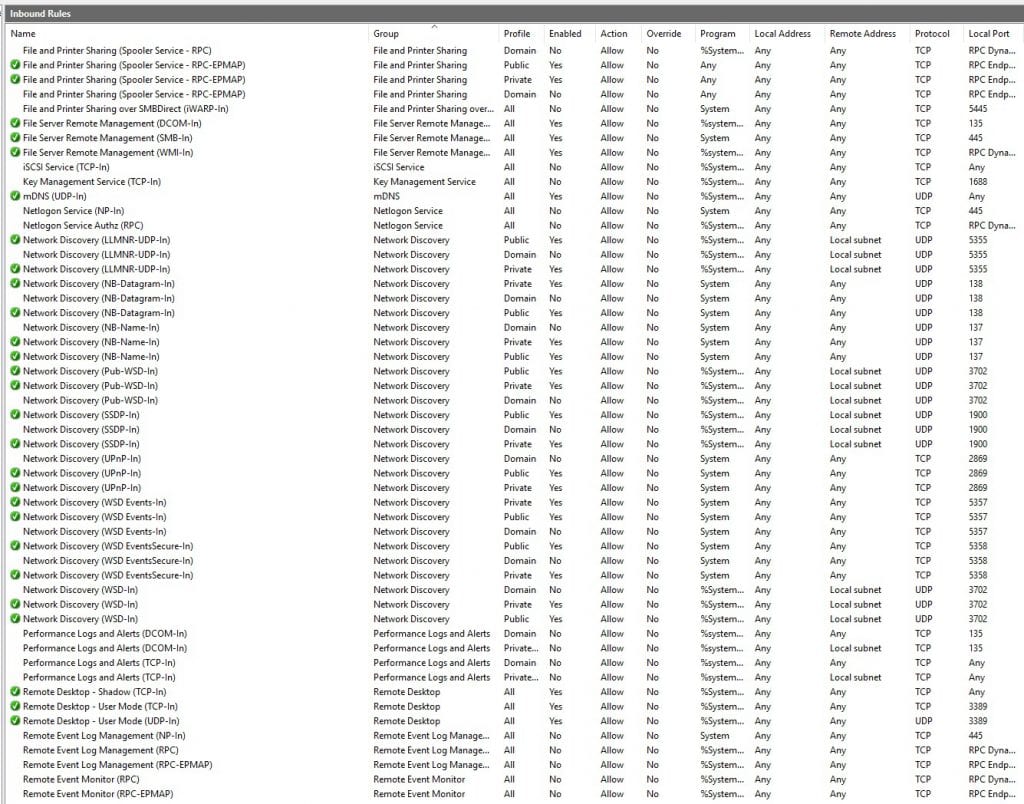
For example, if you would like to change your RDP port to a different one instead of the default “3389,” you will have to modify the following two firewall rules within the “Inbound rule” chain:
Remote Desktop - User Mode (TCP-In)
Remote Desktop - User Mode (UDP-In)
You will then need to modify the affected Windows registry entry to the new value. However, to prevent disasters, make sure to create a full backup of the registry beforehand:
-
Press the WINDOWS button + R (keyboard command).
-
Type “regedit” and press Enter.
-
Click “File” > “Export.”
-
Enter a name for the backup file and click “Save.“
-
Now you can navigate to the following path to set the new RDP port number:
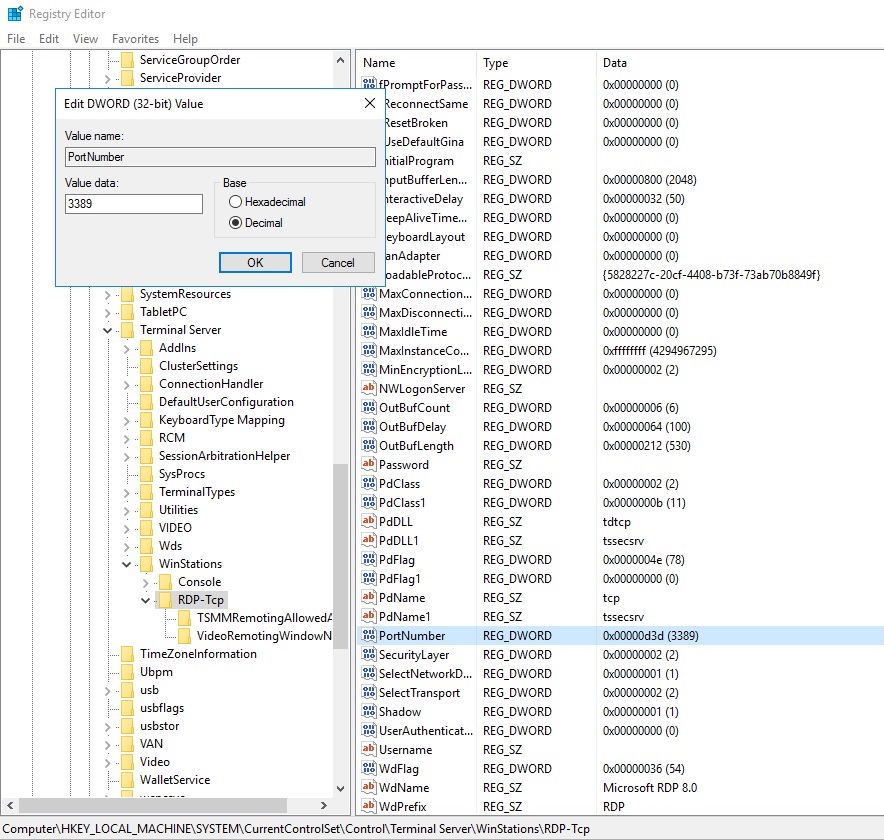
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp\PortNumber
-
Double-click the “PortNumber” registry entry.
-
In the “Value data” field, enter the new port number.
-
Click “OK.“
-
Restart your Windows server.
Now your new RDP port should be active.
Conclusion
Setting up a software firewall is an essential security measure for both Linux and Windows systems. The process is relatively straightforward and can be accomplished using built-in tools on both platforms. By following the instructions in this guide, you can effectively protect your server from unauthorized access and malicious attacks.
