Data loss can occur due to assorted reasons, including hardware failure, natural disasters, or cyber-attacks. To protect and recover valuable data in case of any unforeseen circumstances, it is essential to have a backup strategy in place. This article will discuss the importance of data backup and provide some useful tips and strategies to help you avoid data loss and keep your data safe and secure.
What is a Backup?
A backup is a duplicate of data that is used to recover the data in the event of a data loss. Backups are typically stored in a different location to ensure redundancy. For example, to avoid data loss on your local computer, you can copy all your important data to an external hard drive.
Types of Backups
There are three main types of backups: full backups, incremental backups, and differential backups.
Full Backups:
A full backup is a copy of all your data. This type of backup is the most time-consuming to create, but it is also the most reliable.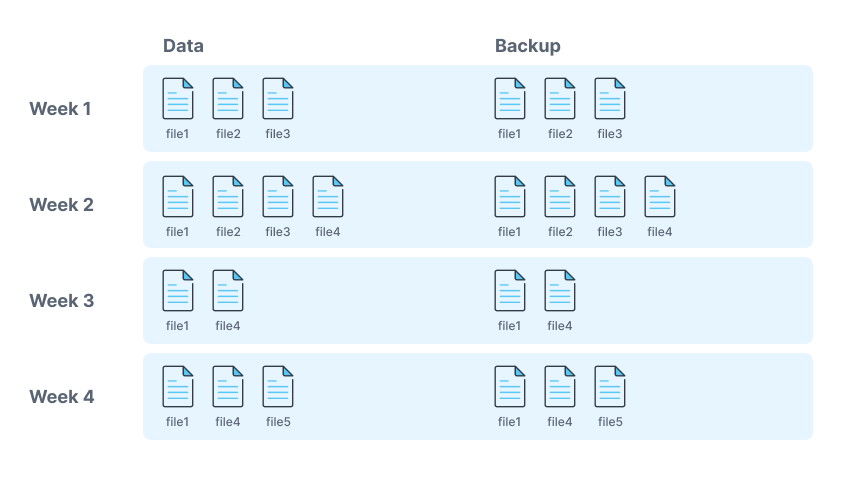
Incremental Backups:
An incremental backup only copies the data that has changed since the last backup. This type of backup is faster to create than a full backup, but it is less reliable because it can be more difficult to restore.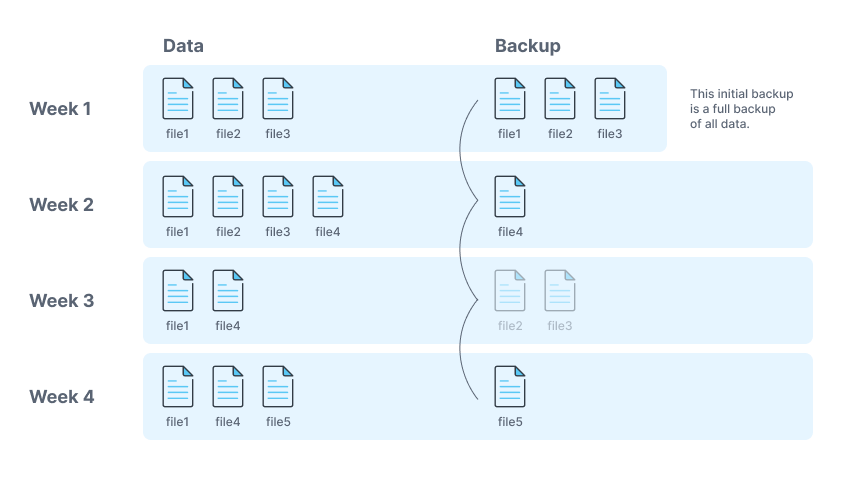
Differential Backups:
A differential backup copies all the data that has changed since the last full backup. This type of backup is faster to create than a full backup, but it is more reliable than an incremental backup because it is easier to restore.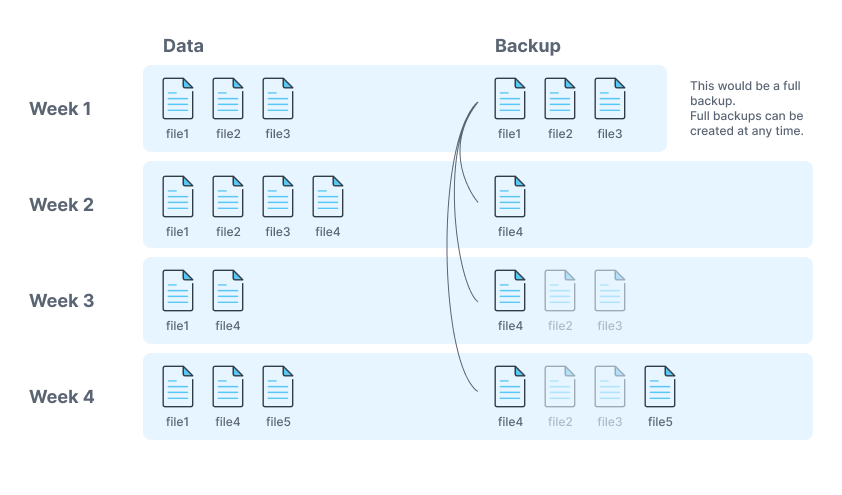
The 3-2-1 Backup Rule
The 3-2-1 backup rule is a simple guideline for protecting your data. It states that you should have at least three copies of your data, stored in two separate locations, and one copy off-site.
-
Local / on-site: This could be the main server or another device at your location.
-
Local / on-site: This should be a different device than the first copy, such as an external hard drive.
-
Off-site: This could be a cloud storage service or another location that is not at your premises.
The reason for having multiple copies of your data is that it protects you from a variety of data loss scenarios. For example, if your local server fails, you can still access your data from the off-site copy.
RAID and Snapshots are not Backups
RAID and snapshots are not backup strategies and do not replace the backup types mentioned above.
-
RAID: RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a way of storing data across multiple disks. This can protect you from data loss if one disk fails. However, RAID is not a backup strategy because it does not protect you from data loss caused by other factors, such as ransomware attacks.
-
Snapshots: Snapshots are a way of taking a point-in-time copy of your data. This can be useful if you need to roll back to the previous state of your data. However, snapshots are not a backup strategy because they are dependent on the host machine and cannot be used to restore on another server.
Backup Storage Options
There are a variety of different storage options available for backups, each with its own pros and cons.
-
External Hard Drives: External hard drives are a popular option for backups because they are inexpensive and easy to use. However, external hard drives can be susceptible to damage, so it is important to handle them with care.
-
Cloud Storage: Cloud storage services, such as Amazon S3 and Google Drive, are a convenient and reliable option for backups. However, cloud storage can be expensive, especially for large amounts of data.
-
Object Storage: Object storage is a type of cloud storage that is optimized for storing copious amounts of data. Object storage is typically more cost-effective than traditional cloud storage, but it can be more difficult to set up and use.
Securing Backups
It is important to secure your backups to protect them from unauthorized access, modification, or deletion. Encryption is a great way to prevent attackers from reading the actual data. There are different tools that can help you with encryption:
- Linux with GnuPG: http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/linux-how-to-encrypt-and-decrypt-files-with-a-password.html
- Windows with VeraCrypt: https://documentation.help/VeraCrypt/Beginner’s%20Tutorial.html
Test and Verify your Backup Strategies
It is important to test your backup strategy on a regular basis to make sure that it is working properly. This involves restoring your data from a backup to make sure that it is complete and uncorrupted.
Conclusion
Data is an invaluable asset that should be protected from loss. By implementing a comprehensive backup strategy, you can safeguard your data from various threats and ensure its availability in case of any unforeseen circumstances. The 3-2-1 backup rule provides a simple framework for creating and maintaining secure backups. Remember to test and verify your backup strategy regularly to ensure its effectiveness. By taking proactive measures to protect your data, you can minimize the risk of data loss and maintain business continuity.

