
Windows Server operating systems present robust capabilities for diverse business and IT functions. However, tailoring these systems to align with specific regional or language preferences can significantly enhance user accessibility and overall productivity. Whether managing Windows Server 2016, 2019, or the latest 2022 edition, the ability to alter the display language remains pivotal.
Changing the Display Language on Windows Server 2016
Commencing with the Windows Server 2016 version:
Login via RDP
To initiate changing the display language, the first step is to log in via RDP. Locate “Remote Desktop Connection” on your local PC, input your IP address and credentials, and click “Connect.”
Adding a New Language via Control Panel
Once connected to your Windows server, press the [Windows] key and search for “Control Panel,” then press [Enter].
Proceed by selecting “Add a language” under “Clock, Language and Region.”
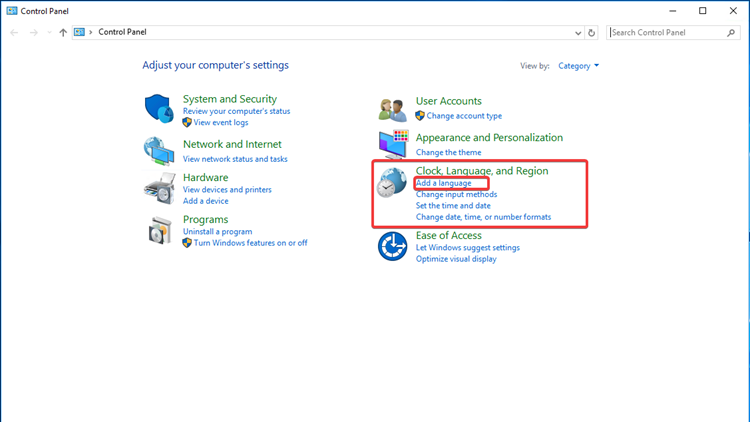
An overview of currently installed languages will be displayed.
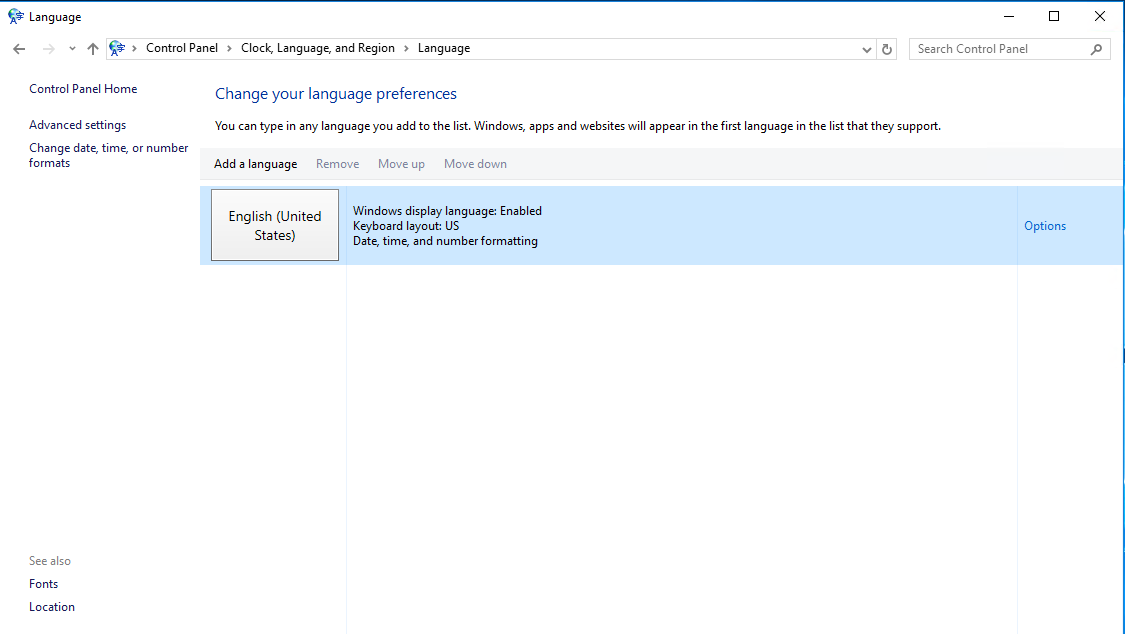
To add a language, click “Add a language.”
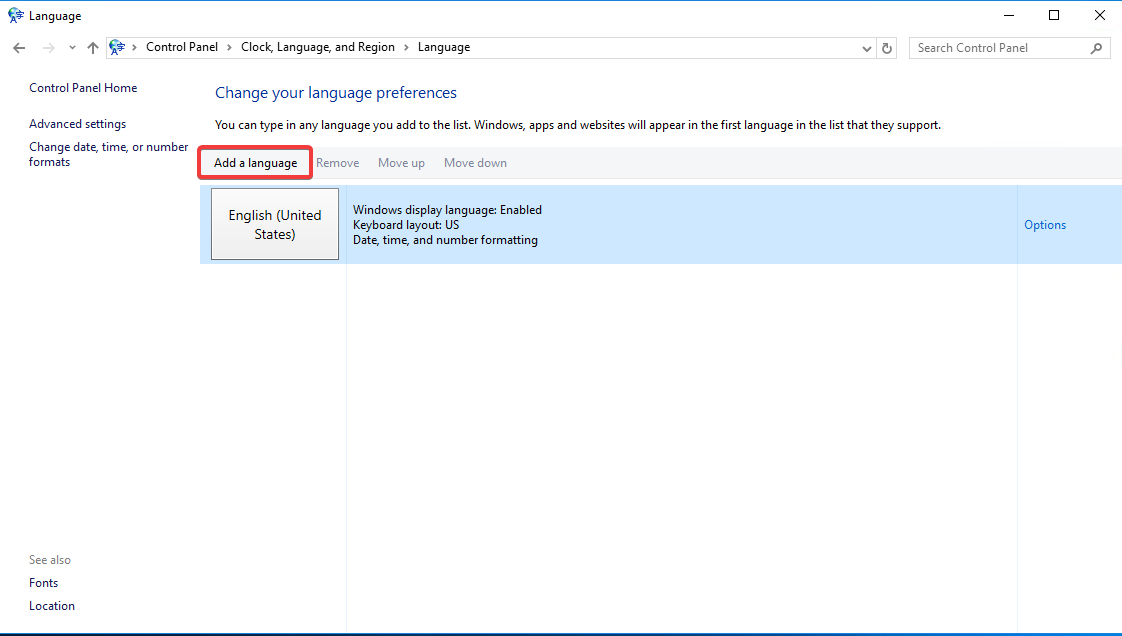
A list of available languages for installation will be presented.
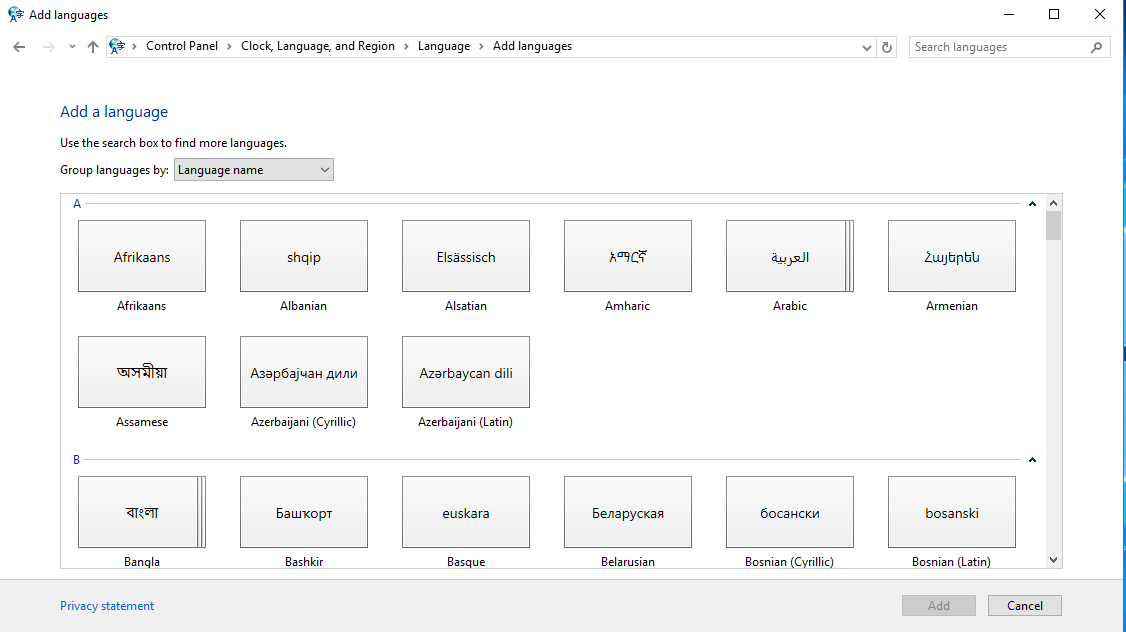
Choose the desired language, for example, “German,” and click “Add.”
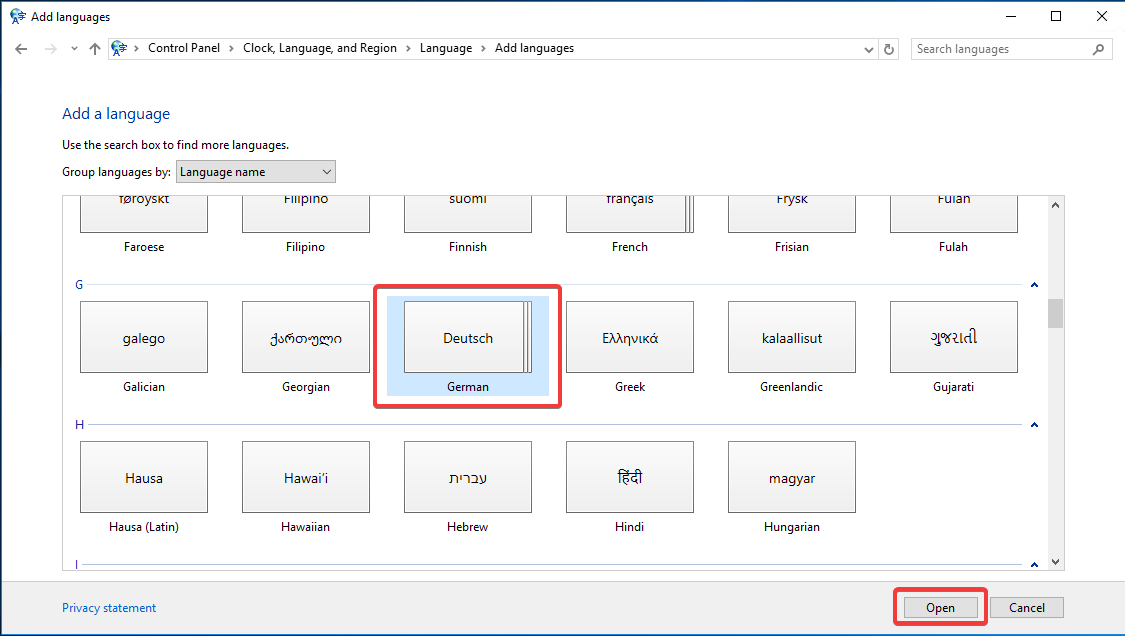
If a language-specific version menu opens after clicking “Open,” select “German (Germany)” and then click “Add.”
The installed language will now appear in the list of available languages.
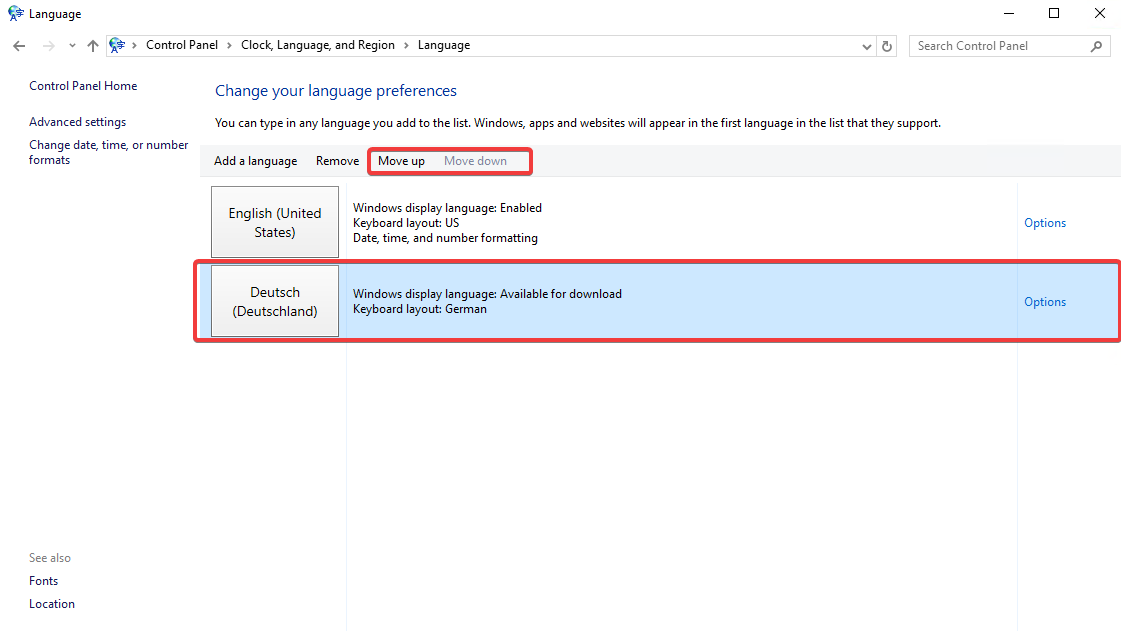
To set the added language as the primary one, use the “Move up” button. This change can be reverted by selecting the language and clicking “Move down.”
Currently, the added language is only available as the keyboard layout but not as the Windows display language. To download the language pack, click “Options,” then select “Download and Install language pack.”
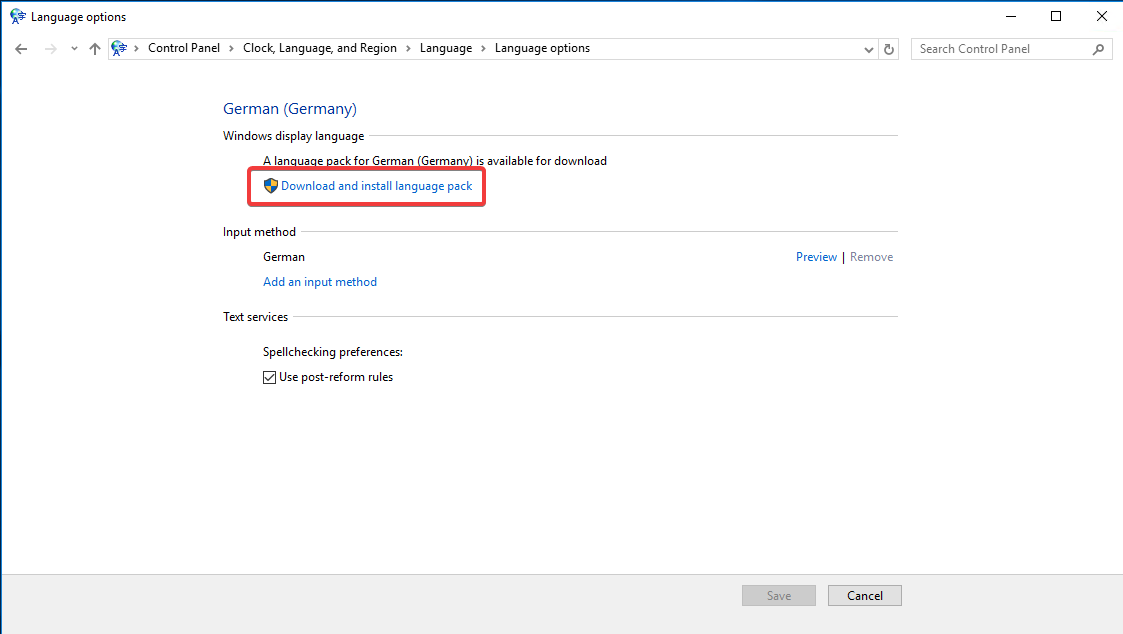
Follow the progress of the download in the displayed window.
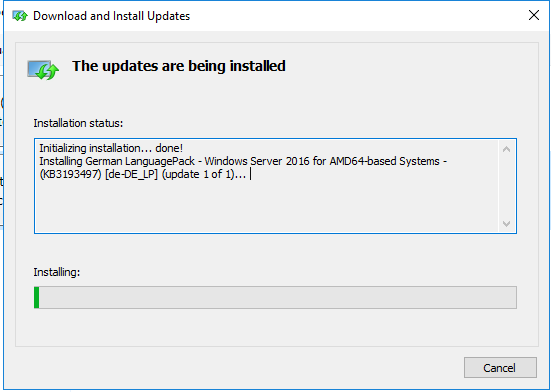
Upon completion of the installation, click “Close.”
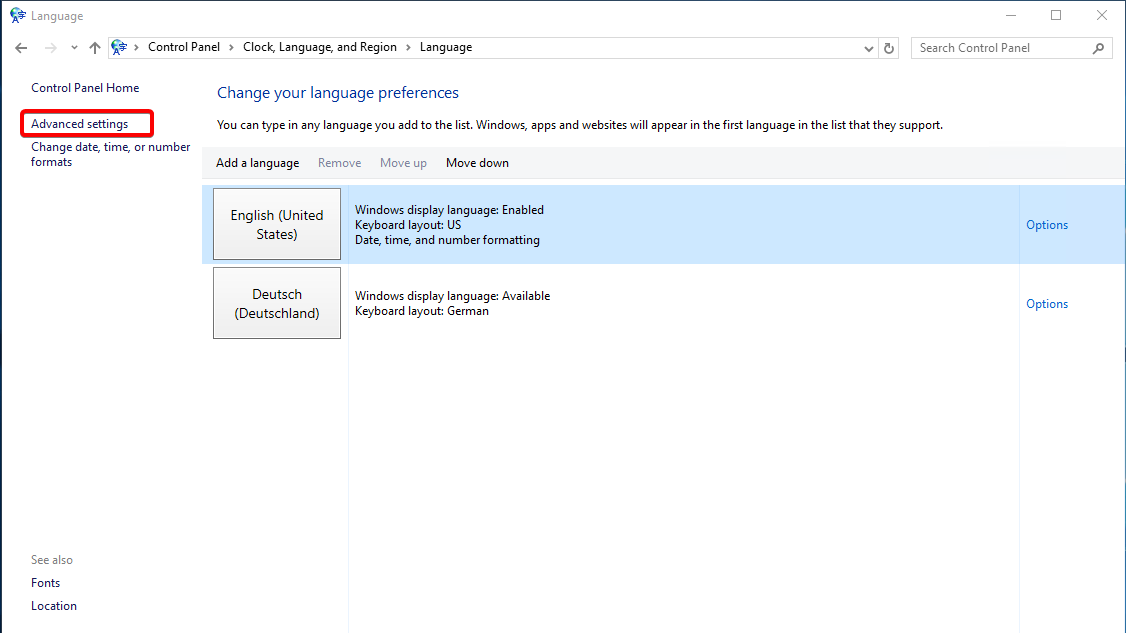
To apply the language changes system-wide, including for new users and the welcome screen, click “Advanced Settings.”
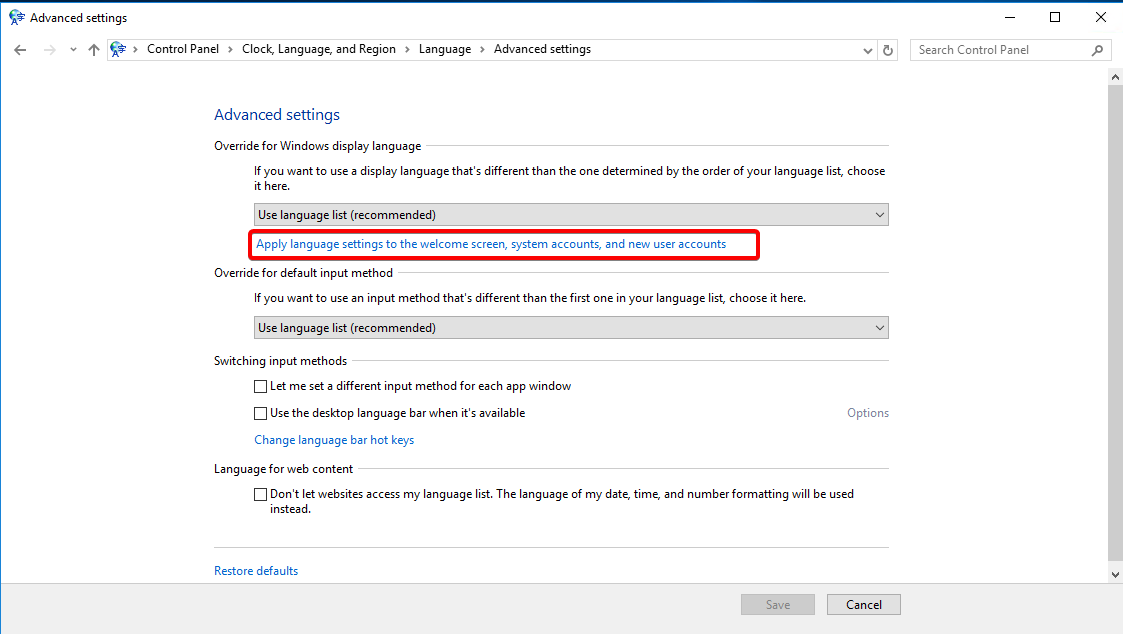
Click “Apply language settings to the welcome screen, system accounts, and new user accounts.”
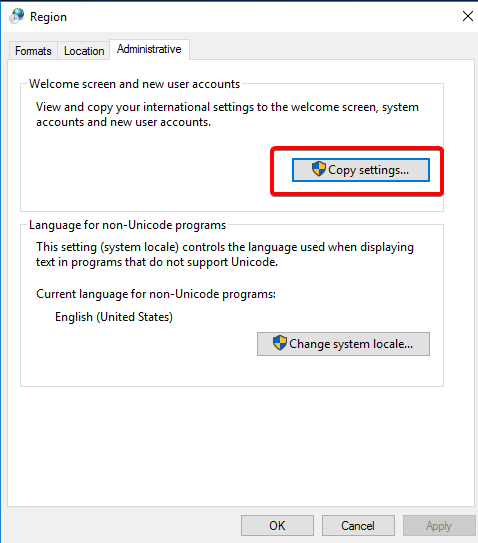
In the new window, select “Copy settings,” tick the boxes for “Welcome screen and system accounts” and “New user accounts,” then click “Ok.”
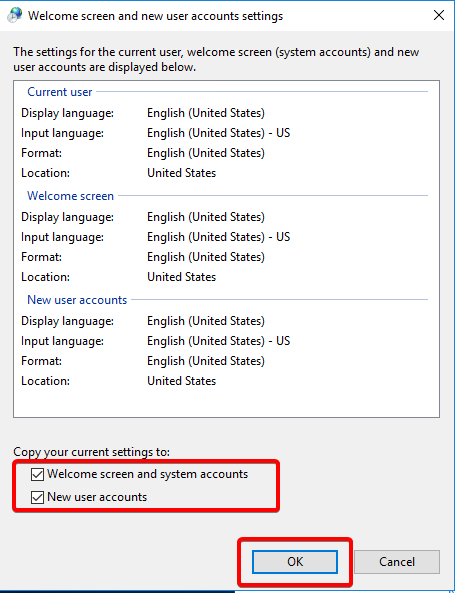
Reboot your server for the changes to take effect.
Changing the Display Language on Windows Server 2019 & 2022
For the two newer versions of Windows server, the methods of changing the display language are identical.
Login via RDP
Similar to Windows Server 2016, log in via RDP. Locate “Remote Desktop Connection,” input your IP address and credentials, and click “Connect.”
Installation of a New Language via Settings
Contrary to Windows Server 2016, the language settings are adjusted through the settings menu for the newer versions. To access settings, search for “Settings” or press [Windows] + [I].
Select “Time & Language,” then choose “Language” from the left menu.
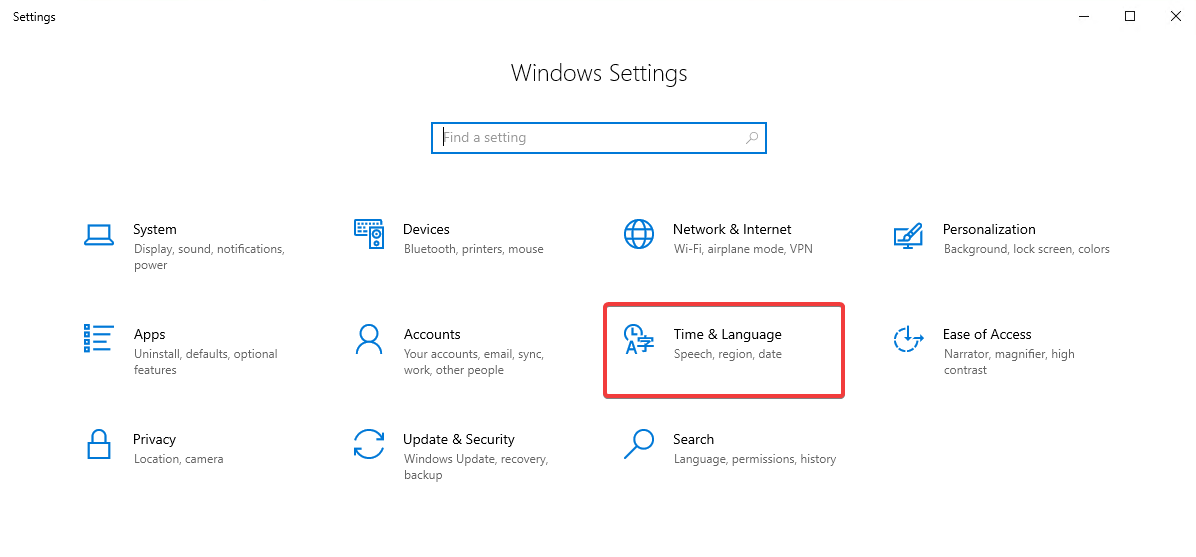
View the currently installed languages in the next window.
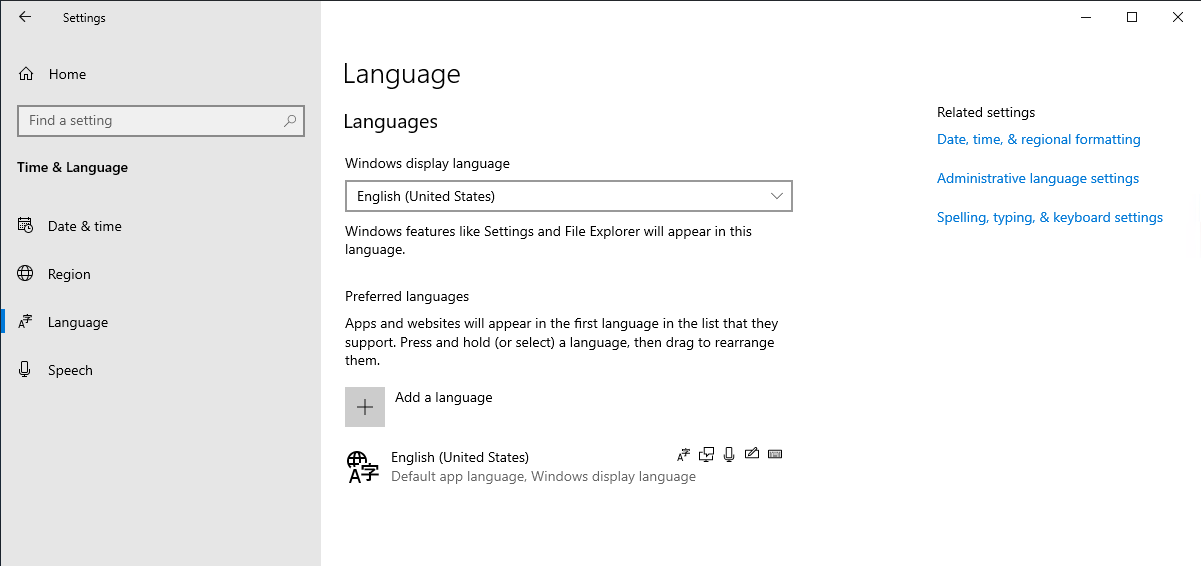
To add a language, click “Add a language” and search for the desired language, such as “German.”

Select the language, then proceed by clicking “Next.”
In the next menu you can select the just mentioned features that you want to install in that language (e.g., Speech, Handwriting etc.)
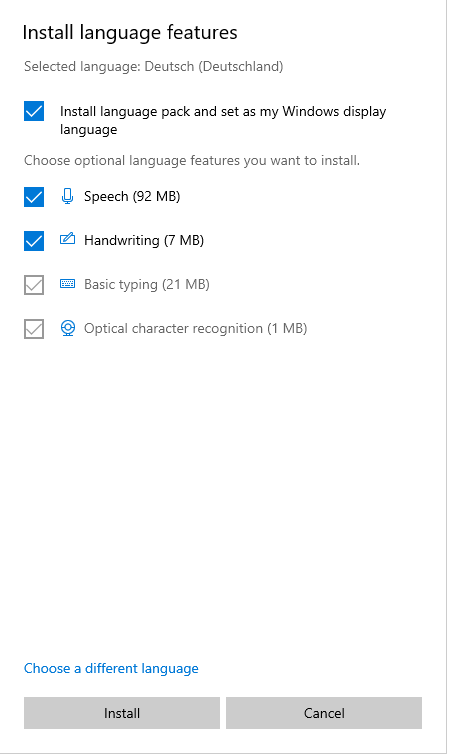
Customize language features and click “Install” to commence the installation.
Now the language will be installed:
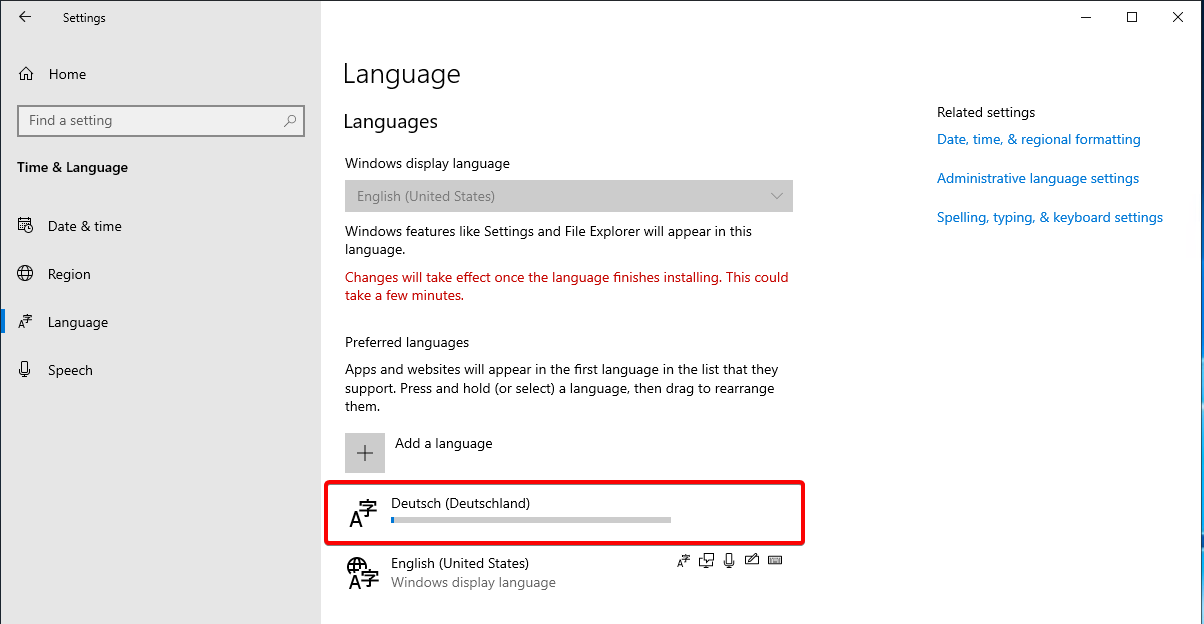
Restart your server after the installation to implement the changes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, configuring the display language on Windows Server systems, whether it’s the older 2016 version or the newer 2019 and 2022 editions, can significantly enhance user accessibility and productivity. Whether adjusting through the Control Panel in older versions or via the Settings menu in the newer iterations, the process remains straightforward.
By following these steps, users can tailor their Windows Server to meet specific language or regional preferences, improving overall usability and accommodating diverse user needs. Implementing these changes system-wide and across user accounts ensures a more inclusive and user-friendly environment, promoting efficiency within various business and IT functions.
