This guide provides an overview of various RAID levels, a data protection technology that helps prevent data loss by storing redundant copies of data across multiple disks. While RAID does not replace regular backups, it offers an additional layer of protection against data loss caused by hardware failures.
Data loss is a common and often costly experience, whether it involves precious vacation photos on an SD card or critical files on a hard drive. Data recovery services can be expensive and time-consuming, making prevention the most cost-effective approach.
Choosing the Right RAID Level
The choice of RAID level depends on factors such as performance requirements, data security needs, and available system resources. Here are some key considerations:
-
Performance: RAID 0 and RAID 10 offer the highest performance, while RAID 5 and RAID 6 provide a balance between performance and security.
-
Data Security: RAID 1 and RAID 6 offer the highest levels of data security, as they can tolerate multiple disk failures without data loss.
-
System Resources: RAID 5 and RAID 6 require more CPU resources due to the need for parity calculations.
RAID Levels Options
-
Hardware RAID: Provides the best performance and security but is more expensive.
-
Software RAID: Offers an easy-to-implement solution for various RAID configurations.
RAID Levels Explained
Based on the evaluation of these factors, you can select the most appropriate RAID level from the available options:
-
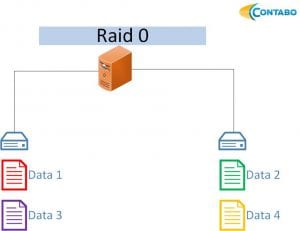
RAID 0: Optimized for performance, RAID 0 distributes data across multiple disks, enhancing both read and write speeds. However, it offers no redundancy, and data loss occurs if any disk fails.

-
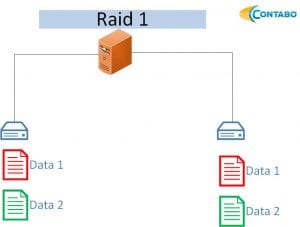
RAID 1: Designed for data redundancy, RAID 1 mirrors data onto a second disk, ensuring data availability even if one disk fails. While it offers excellent protection, it also reduces the usable storage capacity to half of the total.

-
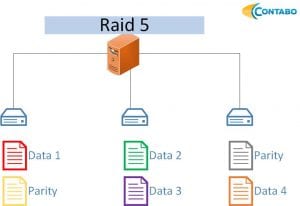
RAID 5: Balancing performance and data security, RAID 5 stripes data across multiple disks and stores parity information on an additional disk. It provides redundancy but requires significant CPU resources due to parity calculations.

-
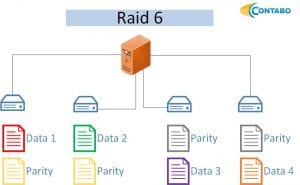
RAID 6: Offering enhanced data protection, RAID 6 mirrors parity information onto two additional disks, ensuring data availability even if two disks fail. However, it consumes even more CPU resources compared to RAID 5.

-
RAID 01: Combining RAID 0 and RAID 1, RAID 01 creates volume groups with RAID 0 striping and mirrors these groups using RAID 1. It provides redundancy but reduces storage capacity to half of the total.

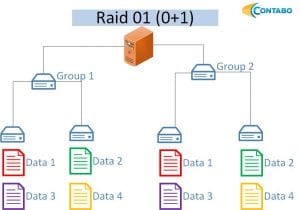
-
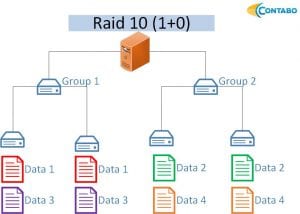
RAID 10: Combining RAID 1 and RAID 0, RAID 10 mirrors volume groups with RAID 1 and stripes these groups using RAID 0. It offers redundancy and performance but reduces storage capacity to half of the total.

Recommendations
-
RAID 5 and RAID 6 are generally not recommended for write-intensive applications due to their high CPU demands.
-
For dedicated servers, additional hard disks or RAID controllers can be ordered at any time.
-
Contact the support team for assistance with specific configuration requirements.
Overview of RAID Levels
The following table provides a summary of the different RAID levels:
| RAID Level | Data Distribution | Disk Redundancy | Storage Capacity | Performance | CPU Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RAID 0 | Striped | None | Maximum | High | Low |
| RAID 1 | Mirrored | 1/n | Half | Improved Read | Low |
| RAID 5 | Parity | 1/n | (n-1)/n | Improved Read and Write | High |
| RAID 6 | Double Parity | 2/n | (n-2)/n | Improved Read | Very High |
| RAID 01 | RAID 0 with RAID 1 Mirroring | 2/n | Half | High Read and Write | Low |
| RAID 10 | RAID 1 with RAID 0 Striping | 2/n | Half | High Read and Write | Low |
RAID Options for Dedicated Servers
Additional hard disks or RAID controllers can be ordered for dedicated servers to enhance data protection and performance. Contact the support team for assistance with custom configurations.
Conclusion
RAID levels offer a range of options to balance performance, data security, and storage capacity. By carefully evaluating your needs and selecting the appropriate RAID level, you can effectively protect your valuable data from loss.

